
"10 Ways AI is Revolutionizing the Food Industry: Transforming the Future of Food"
The food business is evolving. This article purpose is to help predict how AI may impact the future of food industry. Before dwelling the top 10 ways, let me explain the basic terms of AI and what it means. The above diagram depicts how these models it in to the AI.
Artificial Intelligence imitates human behavior by relying on machines to learn and execute tasks without explicit directions on what to output.
Machine learning takes in data like what food users consuming and fit the data to an algorithm, to make predictions like what is trending for example Vegan Food, Steak etc.
Deep learning models uses algorithms in the form of artificial neural networks to provide results for more complex use cases. For example what consumers looking in the vegan industry.
Generative AI is a subset of deep learning that can produce new content based on what is described in the input. The generative AI models can produce language, code, and images as an output for the purpose.
Here are the top 10 ways AI changing the food industry
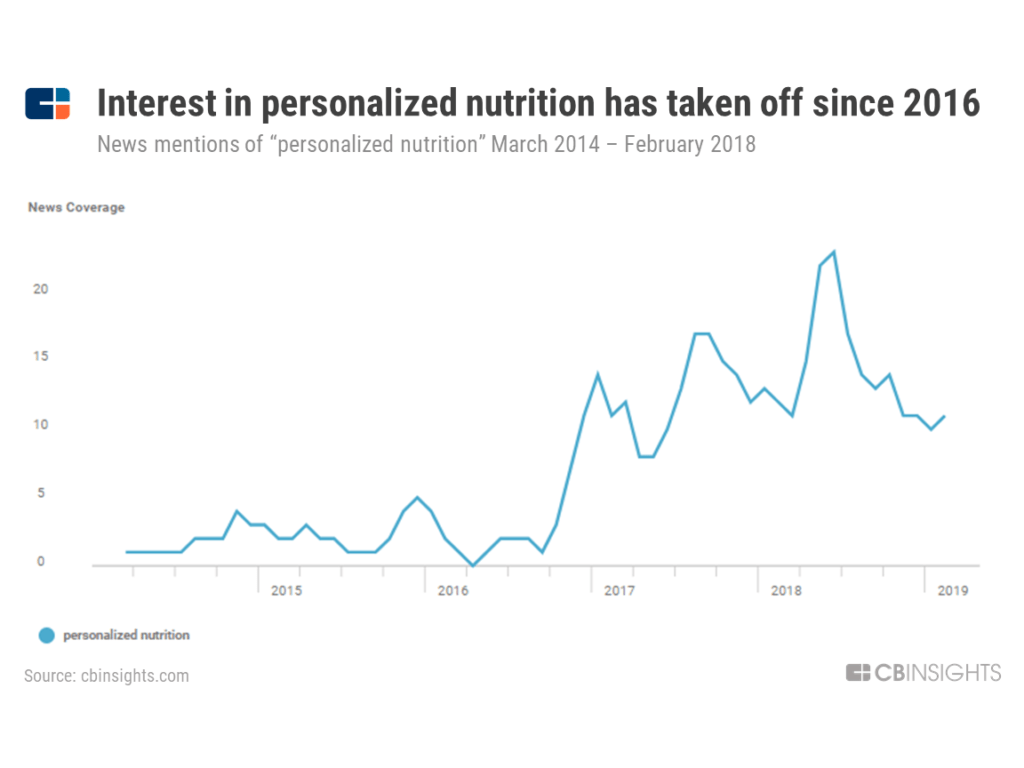
1. Personalized nutrition: Generative AI can be used to analyze an individual's dietary restrictions, health conditions,metabolism, age and recommend personalized nutrition plans based on their unique needs and preferences. This can help people make healthier food choices and achieve their fitness goals more effectively.
2. Precision farming: Deep learning can be used in precision agriculture to optimize crop yields and improve soil quality. By analyzing data from soil sensors, weather forecasts, and satellite imagery, deep learning algorithms can help farmers make data-driven decisions that increase productivity, reduce waste, and improve sustainability.
3. Supply chain optimization: Machine learning algorithms can analyze data on suppliers, logistics, inventory, and demand to optimize the supply chain. This can help food companies reduce waste, minimize stockouts, and improve customer satisfaction.
4. Innovation and product development: AI can analyze market trends, consumer feedback, and ingredient data to identify new product opportunities and develop innovative new products that meet the changing needs of consumers.
5. Sustainable food production: AI can be used to optimize food production and reduce waste by predicting demand, identifying areas where resources can be used more efficiently, and finding new ways to repurpose food waste. This can help to create a more sustainable food system that benefits both the environment and the economy.
6. Predictive maintenance: Machine learning can help food companies predict when equipment is likely to fail, enabling them to schedule maintenance and repairs proactively. This can help reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
7. Food quality and safety: Machine learning algorithms can be used to monitor food production lines and detect anomalies or defects that could pose a risk to consumers. This technology can help food companies ensure that their products meet quality standards and are safe to eat.
8. Quality control and food safety: Deep learning can be used to analyze images and videos of food production lines to detect defects or contaminants that could pose a risk to consumers. This technology can help food manufacturers ensure that their products meet quality standards and are safe to eat.
9. Yield optimization: Deep learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from food production to identify patterns and optimize production processes. This can help food manufacturers maximize their output while minimizing waste, reducing costs, and improving overall efficiency.
10. Growth analytics: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from various sources to identify location for franchise development, foot traffic data, local/global events, menu trends to help local businesses to prosper by helping them to select location, chose/change menu, reduce maintenance and more.
Overall, AI is already transforming the food industry by enabling more efficient, precise, and data-driven decision-making across the entire value chain, from sourcing raw materials to delivering products to consumers.